What we mean by a data specification
A data specification is a formal document that defines how data should be structured, formatted, stored and exchanged in a consistent way.
Each specification provides a set of rules and guidelines for producing and organising that data, ensuring that it can be read and understood by other systems without any confusion or errors.
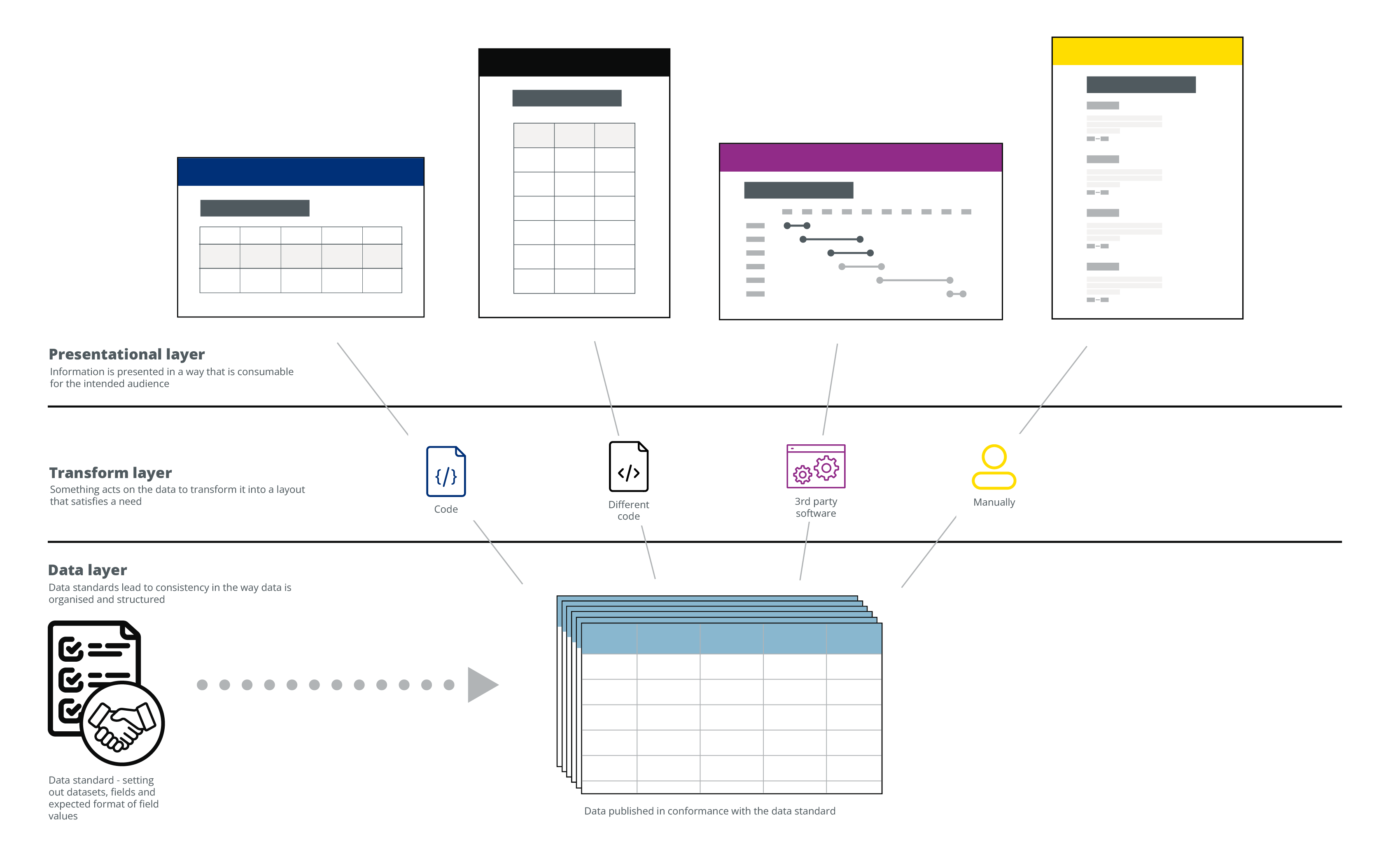
This diagram shows how data specifications are the basis for effective digital ecosystems. Data specifications support the creation of consistent, usable and valuable data. This data can then be relied on to deliver tools and services that satisfy the specific needs of a wide variety of differing users.
What a data specification won’t do
A data specification won’t in itself answer questions for you. It provides the raw ingredients to help you get the answers.
A data specification doesn’t guarantee data quality. The quality of data ultimately depends on how well the specification is implemented and followed, as well as the quality of the data collection process itself.
Standards help shape consistency - but can’t make any judgement in terms of accuracy. For example it can fix spelling errors, but can’t tell whether a site has been entered in the correct location.
Data specifications are not fixed or static, they evolve. A data specification needs to be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
A data specification doesn’t describe how the data should be used. It is more about how the data is organised and structured behind the scenes than how it should be presented when shown to people.